.png)
When it comes to AI-powered quality inspection in manufacturing, Edge AI and Cloud AI serve different purposes. Here's a quick breakdown:
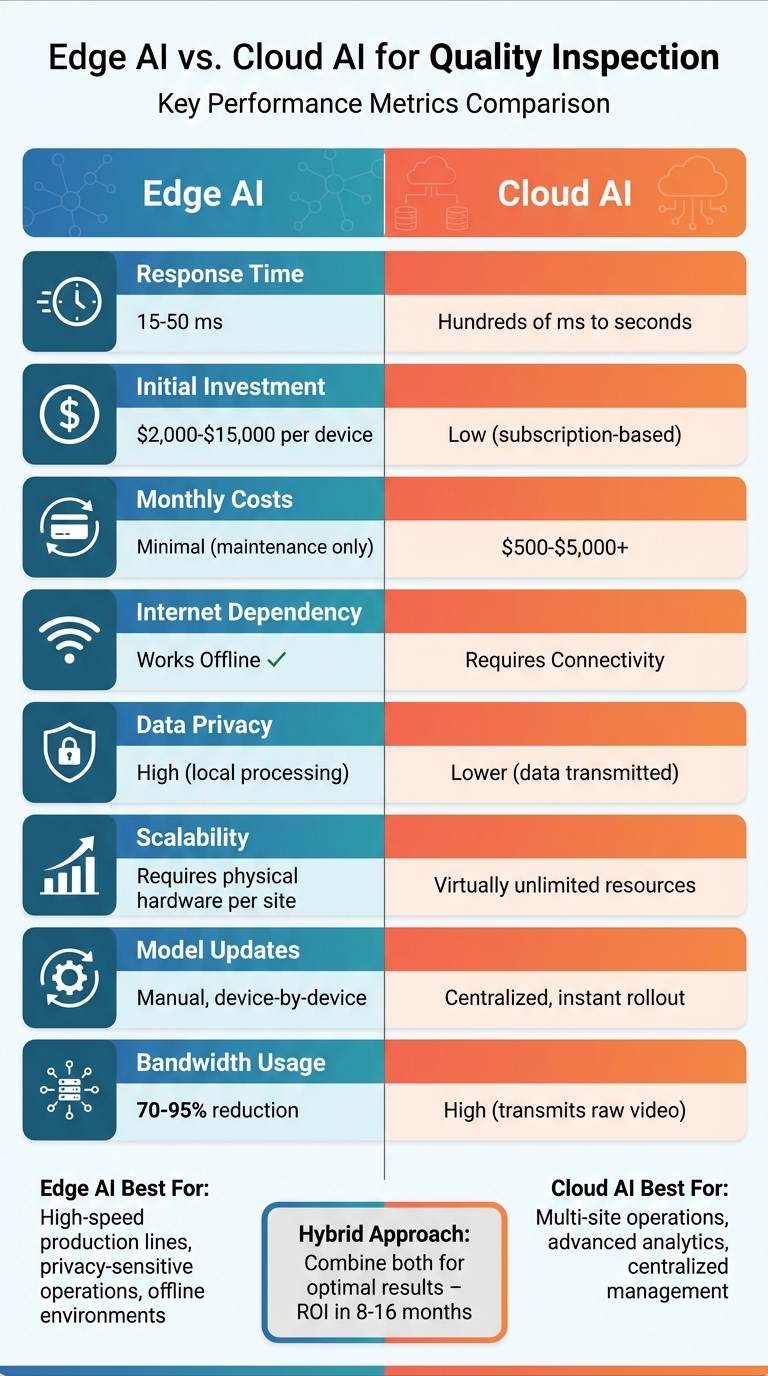
| Factor | Edge AI | Cloud AI |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | 15–50 ms | Hundreds of ms to seconds |
| Initial Cost | $2,000–$15,000 per device | Low (subscription-based) |
| Monthly Cost | Minimal (maintenance) | $500–$5,000+ |
| Internet | Works offline | Needs stable connectivity |
| Data Privacy | High (local processing) | Lower (data transmitted) |
| Model Updates | Manual | Centralized, instant rollout |
For most manufacturers, a hybrid approach - combining Edge AI's speed with Cloud AI's analytics - strikes the right balance.
Edge AI vs Cloud AI Quality Inspection Comparison Chart
Edge AI handles data directly at the source - whether it's sensors or cameras on the production line - eliminating the delays caused by sending data back and forth to remote data centers. With response times ranging from 15 to 50 milliseconds, it easily outpaces cloud processing, which often lags behind with delays of 1 to 2 seconds. For industries relying on high-speed production, this difference is critical.
Take a packaging line running at over 100 parts per minute: even a one-second delay could allow more than 30 defective products to pass through unnoticed. Many factory systems require decision-making speeds of 10 to 20 milliseconds or faster to stop defects in their tracks - whether by rejecting faulty items or pausing the line altogether. This speed is what makes edge AI so reliable for high-speed automation.
"Cloud processing rarely achieves sub-100ms response times in industrial settings, but factory automation often requires 10-20ms or faster decisions." - VarTech Systems
One of the standout features of edge AI is its independence from constant internet connectivity. Even during network outages or in facilities with spotty internet, edge AI keeps quality inspections running smoothly. This means production lines don't grind to a halt because of a cloud service disruption or a regional connectivity issue.
By processing data locally, edge AI reduces bandwidth usage by a staggering 70% to 95%. Instead of streaming full-resolution images, it sends only essential data summaries. For facilities with limited bandwidth or unreliable infrastructure, this is a game-changer, ensuring operations remain uninterrupted even in challenging conditions.
Edge AI processes data locally, keeping sensitive manufacturing information securely on-site. This eliminates the need to transmit data over external networks, significantly reducing the risk of cyberattacks during data transfers. For manufacturers dealing with strict regulations like GDPR, ITAR, or HIPAA, this localized processing simplifies compliance.
In fact, 53% of organizations adopt edge AI specifically to enhance data privacy and security. This approach is especially vital for protecting intellectual property, such as high-value trade secrets or sensitive defense-related manufacturing processes.
"Edge architecture offers enhanced privacy by processing sensitive data directly on the device, whereas cloud AI entails transmitting data to external servers, potentially exposing sensitive information to third-party servers." - IBM
Cloud AI acts as a central hub for managing machine learning models across an entire operation. With it, manufacturers can roll out updates to models at all locations in just minutes. For instance, when a new defect type is identified or a bug needs fixing, data scientists can deploy updates directly from a central server - no need to visit the factory floor.
Cloud platforms also provide virtually limitless computing and storage resources, scaling automatically to meet demand. This flexibility mirrors the rapid growth of the global cloud AI market, which is expected to soar from $78.36 billion in 2024 to $589.22 billion by 2032, achieving a 28.5% compound annual growth rate.
"Centralized models can be updated without physically accessing devices, enabling rapid iteration and global deployment." - Clarifai
This centralized model lays the foundation for integrating advanced analytics into cloud-based systems.
Building on centralized management, cloud AI excels at consolidating data from multiple sources. By pooling information from various production lines and facilities into a single repository, manufacturers can perform in-depth analytics that uncover patterns otherwise invisible at the local level. This capability supports quicker root cause analysis, predictive maintenance, and identifying supply chain trends.
For example, one automotive manufacturer using a cloud-based AI quality management system achieved a 30% reduction in quality-related costs and boosted customer satisfaction by 20%. Similarly, Foxconn reported an 80% improvement in defect detection rates and a 30% reduction in inspection time with AI-driven visual inspection. These systems also reduce the need for human-labeled images by up to 300 times compared to general-purpose platforms, significantly speeding up deployment timelines.
"Cloud-QMS solutions are the backbone of the AI revolution in quality management. They provide a centralized platform for data storage, analysis, and collaboration." - Qualityze
Cloud AI eliminates the need for expensive on-site hardware, which can range from $2,000 to $15,000 per deployment. Instead, it operates on subscription-based models costing between $500 and $5,000 or more per month.
This shift from capital expenditure to operating expenses simplifies budgeting and reduces financial risks. Cloud providers take care of infrastructure upgrades, security updates, and maintenance, allowing internal IT teams to focus on production rather than server management. For multi-site operations, this centralized approach provides access to high-level processing power without the need for significant on-site investments at each location.
"Plant managers gained access to processing power and storage previously requiring massive on-site server investments. Centralized data centers replaced the need for on-site database administrators." - VarTech Systems
Unlike Edge AI, cloud AI transforms hardware investments into flexible, subscription-based operational costs, offering a more efficient and scalable solution.
Let’s break down the key differences between Edge AI and Cloud AI. Choosing the right approach boils down to your specific needs, budget, and how you prioritize operations. Each has its strengths, so understanding the trade-offs is crucial for making the best decision.
When it comes to response time, Edge AI stands out with near-instant results, while Cloud AI lags behind due to its reliance on network connectivity.
Looking at costs, the two approaches have very different structures. Edge AI requires a larger upfront investment for hardware, but ongoing costs are minimal. On the other hand, Cloud AI has a lower initial cost but comes with recurring fees ranging from $500 to $5,000+ per month. For Edge AI, the typical return on investment (ROI) is achieved within 8 to 16 months.
Reliability is another major factor. Edge AI operates independently of the internet, making it ideal for environments where connectivity is unreliable. In contrast, Cloud AI relies on constant internet access, and any disruption can halt operations. Additionally, Edge AI significantly reduces bandwidth usage - by 70% to 95% - since it only transmits critical alerts instead of raw data streams.
Here’s a quick comparison of the two:
| Factor | Edge AI | Cloud AI |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | 15–50 milliseconds | Hundreds of ms to several seconds |
| Initial Investment | $2,000–$15,000 per deployment | Low (subscription-based) |
| Monthly Costs | Minimal (maintenance only) | $500–$5,000+ depending on usage |
| Internet Dependency | Operates offline | Requires continuous connectivity |
| Bandwidth Usage | Low (70–95% reduction) | High (transmits raw video) |
| Scalability | Requires physical hardware per site | Virtually unlimited virtual resources |
| Data Privacy | High (data stays on-premises) | Lower (data transmitted externally) |
| Model Updates | Device-by-device deployment | Centralized, instant rollout |
| Best For | High-speed production lines | Multi-site analytics and training |
Each approach has its ideal use case. Edge AI shines in scenarios requiring ultra-fast response times and offline reliability, like high-speed production lines. Meanwhile, Cloud AI is better suited for tasks like multi-site analytics and centralized model updates.
Building on earlier discussions about its performance benefits, let's explore specific scenarios where Edge AI truly shines. Some manufacturing environments demand local processing to achieve optimal quality inspection results.
In fast-paced production settings, timing is everything. Edge AI can process images in as little as 15 to 50 milliseconds. For instance, on a high-speed packaging line, even a one-second delay could mean over 30 defective products make it through. Industries like steel manufacturing, where coils move at 300 feet per minute, or packaging operations handling 60 parts per second, depend on decision-making under 100 milliseconds. By placing Edge AI hardware directly on the production line, it analyzes defects in real time and integrates seamlessly with PLCs and SCADA systems to trigger reject mechanisms instantly.
For manufacturers dealing with sensitive data, Edge AI offers a secure solution by keeping all processing local. This setup is invaluable for facilities working with proprietary designs, defense components regulated under ITAR, or medical devices subject to HIPAA compliance. Since data never leaves the facility, risks associated with transmission are eliminated. Additionally, each edge device operates as a self-contained unit, reducing the potential impact of cyberattacks compared to centralized cloud systems. Beyond security, Edge AI also addresses operational challenges like limited bandwidth, making it a practical choice for these environments.
In facilities with limited connectivity or high bandwidth costs, Edge AI ensures uninterrupted quality inspection. By transmitting only critical alerts or summary data instead of raw video streams, it reduces bandwidth needs by 70% to 95%. For operations dealing with expensive or restricted bandwidth, this efficiency directly cuts costs while maintaining comprehensive inspection capabilities.
Cloud AI shines when centralized control and in-depth data analysis are priorities. It's especially useful for companies operating multiple facilities or those heavily focused on long-term analytics.
Managing quality inspection across multiple locations becomes much smoother with Cloud AI. It allows for simultaneous updates across all facilities, avoiding version mismatches and reducing the need for on-site engineers. For instance, when a new defect type is identified or a model upgrade is ready, updates can be deployed to every factory site within minutes - no physical hardware access required. This centralized approach not only simplifies operations but also enables deeper, more comprehensive analytical insights.
Cloud AI's advanced batch analytics are a game-changer for identifying long-term trends in manufacturing quality. By processing historical data, it can uncover patterns that individual devices might miss. For example, Ford utilized Google Cloud's Visual Inspection AI at its stamping stations to detect defects in metal sheets. The cloud-based system ran specialized models capable of analyzing complex surfaces. This technology can handle massive datasets, processing petabytes of archived images to reveal trends like seasonal quality fluctuations or supplier-specific issues. Similarly, FIH Mobile, a subsidiary of Foxconn, used Google Cloud's Visual Inspection AI to maintain high-quality standards for printed circuit boards, identifying issues such as misplaced screws and soldering errors. These capabilities make cloud systems a strong choice in environments with stable internet connectivity.
Cloud AI is most effective in facilities with reliable, high-speed internet. In settings where a 1–2 second processing delay doesn’t disrupt production safety or efficiency, cloud-based inspection can eliminate the need for costly on-site GPU hardware. For manufacturers in the prototyping or pilot phase, cloud APIs offer a low-cost way to test and validate use cases without committing to significant hardware investments upfront. This flexibility allows businesses to experiment and refine their processes before scaling up.
For manufacturers aiming to optimize cloud AI for quality inspection, expert integration services - like those provided by Artech Digital - can help create tailored solutions that improve operational workflows and efficiency.
Manufacturers can take advantage of both Edge and Cloud AI to enhance quality inspection processes. A hybrid approach combines real-time decision-making at the edge with cloud-based analytics and model training, offering a balanced solution. Edge devices handle immediate quality control on the production floor, while the cloud handles more complex tasks like model updates and long-term analysis.
This setup helps manage bandwidth efficiently by processing data locally and only sending critical alerts to the cloud. For instance, a high-speed inspection station equipped with 30 5MP cameras generates about 450 MB/s of data - well beyond the capacity of a standard gigabit Ethernet connection, which maxes out at 125 MB/s. By filtering data at the edge, you reduce network strain while still collecting meaningful insights.
The real power of hybrid systems lies in their ability to improve continuously. Edge devices flag images with uncertain results - those with confidence scores between 0.4 and 0.7 - and send them to the cloud for human review and model retraining. This creates a feedback loop that refines the inspection system over time. In June 2025, UnitX reported that a global battery manufacturer deployed an AI inspection system across over 10 production lines in the U.S., achieving 99.78% accuracy and 99% uptime while inspecting one million cells.
"Data insight does not stop at the walls of factories." - Keven Wang, CEO at UnitX
The following sections break down how hybrid systems combine edge-based real-time decisions with cloud-powered analytics.
In a hybrid setup, edge devices ensure seamless real-time decision-making, even if network connectivity drops. When a product moves under an inspection camera, the edge device processes the image in just 15 to 50 milliseconds. This speed is crucial for high-speed production lines, where cloud latency of 1 to 2 seconds could allow defective products to slip through. The edge device makes immediate pass/fail decisions, activating reject mechanisms or alerting operators without relying on the cloud.
This local processing ensures continuous production during internet outages. Even if connectivity is lost, the inspection system keeps running on the last deployed model until the network is restored. This resilience minimizes downtime and keeps production on track.
While edge devices handle immediate tasks, the cloud provides the computing power needed for advanced model training and large-scale data analysis. Training sophisticated neural networks requires significant processing capabilities that aren’t feasible to deploy at every inspection station. The cloud aggregates data from all edge devices, identifies defect trends, and retrains models to improve accuracy.
For example, in early 2021, FIH Mobile, a Foxconn subsidiary, used Google Cloud's Visual Inspection AI for printed circuit board assembly. This project achieved 10x better accuracy than traditional machine learning methods and created highly accurate models using as few as 10 to 20 defective images. Such advanced model development thrives in the cloud, where vast computing resources make it possible to process petabytes of historical data, uncovering patterns like seasonal quality variations or supplier-specific issues.
Hybrid systems rely on the cloud as a central control hub to manage model updates and push them to edge devices. Once a model is retrained and validated in the cloud, it can be deployed across all inspection stations with over-the-air (OTA) updates.
This centralized approach is especially useful for manufacturers with multiple facilities. For example, a model improvement discovered at one plant can be rolled out to all locations in minutes. New models can also run in shadow mode on edge devices, analyzing products without triggering actual reject decisions. This allows manufacturers to test model accuracy in real-world conditions before fully activating the update. This method reduces risk and ensures smooth transitions when upgrading inspection systems.
For manufacturers considering hybrid edge-cloud solutions, Artech Digital offers custom AI integration services to design and deploy systems tailored to your production needs and quality inspection goals.
Selecting the right AI approach depends on factors like line speed, network reliability, and data privacy requirements. For production lines operating at speeds over 100 parts per minute, Edge AI is crucial to catch defects before they progress further down the line. Cloud AI simply can't keep up with the latency demands of high-speed manufacturing. These considerations highlight the key trade-offs we've explored throughout this article.
"The closer your AI is to the moment of action, the more value it can deliver." - Oleg Tagobitsky, CEO, API4AI
A practical way to start is by using cloud-based APIs to validate your use case. This allows you to experiment and prove the model works without committing to the $2,000–$15,000 investment required for edge hardware. Once your prototype succeeds, you can transition to edge devices for production, saving unnecessary upfront costs.
For manufacturers with multiple facilities, a hybrid approach can be highly effective. Edge devices manage real-time decision-making on-site, while the cloud handles tasks like updating models, consolidating data, and analyzing trends. This setup combines the strengths of both methods and typically delivers a return on investment within 8–16 months. Over a 3- to 5-year period, edge AI often proves more cost-efficient, as its higher initial costs are offset by avoiding the rapidly escalating monthly fees of cloud AI - these can exceed $5,000 for high-throughput operations.
For facilities facing extreme conditions, unreliable connectivity, or stringent privacy rules like GDPR or ITAR, Edge AI is the better choice. Drawing on the analysis above, manufacturers looking to adopt AI for quality inspection can turn to Artech Digital for custom solutions tailored to their production environments and inspection needs.
The cost of implementing Edge AI for quality inspection primarily involves an upfront investment in hardware like edge devices, cameras, and servers. While this increases capital expenditure (CapEx) initially, it helps cut down on ongoing costs by removing the need for recurring fees tied to cloud services, data transfer, or per-inference charges. Although hardware maintenance costs might arise, they tend to be predictable over time.
On the other hand, Cloud AI keeps initial hardware costs low - usually requiring just basic cameras and network connectivity. However, it leads to higher operational expenditure (OpEx) due to ongoing expenses for data storage, computing resources, and bandwidth. In high-volume or latency-sensitive environments, these recurring costs can quickly outpace the one-time investment in Edge AI hardware.
For large-scale, real-time quality inspection, Edge AI often proves to be the more cost-efficient option. Meanwhile, Cloud AI might be a better fit for smaller-scale operations or scenarios where real-time processing isn't critical. Artech Digital specializes in helping manufacturers assess these options and implement the most budget-friendly solution tailored to their specific needs.
A hybrid Edge-Cloud AI approach merges the immediacy of Edge AI with the flexibility and analytical power of cloud computing. By processing data right on edge devices - like cameras or sensors - defects can be identified in mere milliseconds. This ensures high-speed production lines stay on track without interruptions. At the same time, the cloud takes care of tasks like compiling data, retraining AI models, and performing deeper analysis, paving the way for continuous improvement.
This setup allows manufacturers to strike a balance between speed, efficiency, and scalability. Critical tasks, such as detecting defects, are handled locally to prevent production slowdowns. Meanwhile, less time-sensitive processes, like analyzing trends or planning predictive maintenance, are managed in the cloud. Additionally, this method minimizes bandwidth usage, keeps sensitive data secure by storing raw images on-site, and enables easy updates to AI models across multiple locations. Artech Digital specializes in crafting and implementing these hybrid AI systems, delivering dependable, real-time quality checks for a variety of manufacturing needs.
When choosing between Edge AI and Cloud AI for quality inspection, manufacturers need to weigh several important factors:
Artech Digital helps manufacturers navigate these considerations by offering customized AI solutions. They integrate edge computing for real-time defect detection with cloud-based tools for advanced analytics and model updates, ensuring efficient and scalable operations tailored to U.S.-based manufacturers.
.png)

