
AI systems come with unique risks, such as data poisoning and biased outcomes, which require specialized security standards. Global organizations are increasingly adopting frameworks like NIST AI RMF, ISO/IEC 27001, and the EU AI Act to address these challenges, manage risks, and comply with emerging regulations. These standards help ensure AI systems are secure, reliable, and aligned with ethical principles while safeguarding data and reducing operational risks.
Key takeaways:
Organizations must audit systems, create clear security policies, and train teams to handle AI-specific threats. Early implementation of these standards not only reduces risks but also builds trust and positions businesses for growth in a regulated environment.
Global organizations need AI security standards to tackle technical vulnerabilities and maintain a strategic edge. With 85% of companies already using AI services, the stakes are high, especially when 25% of organizations face visibility gaps that traditional cybersecurity measures can’t address. These blind spots expose businesses to risks that conventional approaches fail to mitigate.
AI introduces unique threats - like data poisoning and prompt injection - that can manipulate outputs and bypass standard security tools. SentinelOne highlights this challenge:
"AI security standards have changed the way we approach cybersecurity... Every organization uses its own specific AI security framework which means they have their own unique challenges to deal with."
By 2026, half of global governments will require organizations to comply with AI laws and data privacy regulations. Failing to adopt recognized frameworks not only invites legal repercussions but also erodes customer and investor trust, especially after security breaches or biased outcomes. These risks extend beyond technology, impacting data protection and compliance efforts.
AI systems open up new vulnerabilities. For example, training data poisoning can introduce flaws by embedding unreliable information. Poor sandboxing practices risk leaking sensitive data, while reliance on pre-trained models increases supply chain vulnerabilities that threaten system integrity.
Guidance like NIST AI 600-1 addresses these challenges by identifying 13 specific risk areas and recommending over 400 actionable steps. These include secure software development practices and continuous monitoring to safeguard data integrity throughout the AI lifecycle.
Different regions approach AI regulations differently. The EU leans on a risk-based framework, while the US focuses on fostering innovation. AI security standards help bridge these gaps by aligning internal risk management practices with international regulatory frameworks. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework serves as a baseline for meeting diverse global requirements. As NIST explains:
"Technical standards in shaping development and use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)... establishes a plan for global engagement on promoting and developing AI standards guided by principles set out in the NIST AI Risk Management Framework."
Standards like NIST SP 800-218A also integrate "security by design" principles into AI development. Features like digital watermarking and metadata tracking help organizations comply with emerging laws on synthetic content labeling. These measures reduce the likelihood of operational disruptions and protect reputations.
Strong AI security standards go beyond compliance - they ensure smooth operations and safeguard credibility. Without them, organizations risk automation failures, model drift, and service outages, which can lead to bad decisions and tarnished reputations. For instance, in 2024, video generation platform Synthesia implemented a contextualized alert system that improved vulnerability management and provided full visibility into their AI infrastructure. Martin Tschammer, Head of Security at Synthesia, explained:
"Our previous security solution attempted to contextualize alerts, but the information provided was unclear. Without that, we weren't able to prioritize remediation."
Bias in AI outcomes poses another reputational risk. Adopting recognized frameworks like ISO/IEC 42001 and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework signals a commitment to managing both technical and ethical risks effectively. This not only protects organizations but also builds trust among stakeholders.
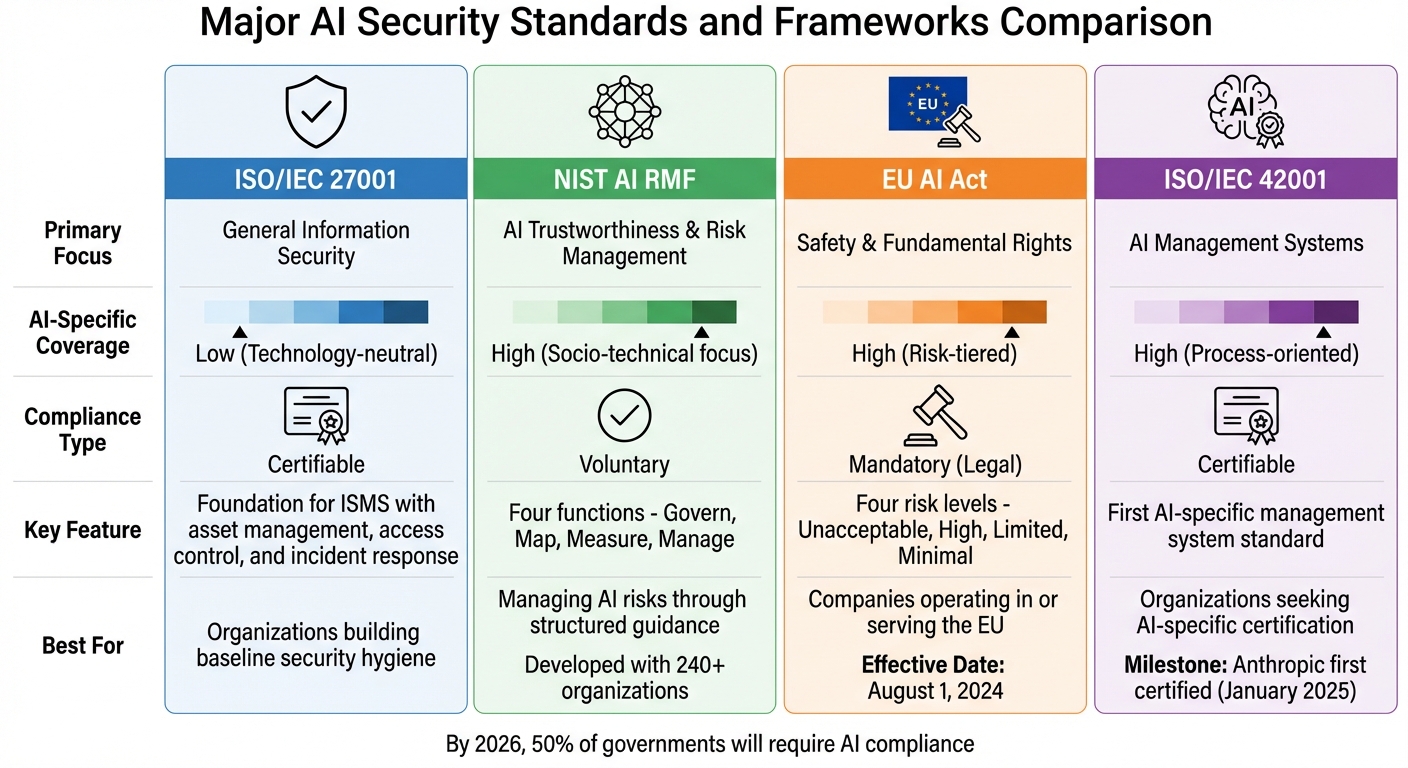
Comparison of Major AI Security Frameworks: ISO/IEC 27001, NIST AI RMF, EU AI Act, and ISO/IEC 42001
Navigating the world of AI security frameworks can feel like tackling a maze. From foundational security practices to AI-specific regulations, organizations must juggle various standards to safeguard their systems. Key players in this space include ISO/IEC 27001, which lays the groundwork for security hygiene, NIST's AI Risk Management Framework, which focuses on trustworthiness, and the EU AI Act, which enforces legal requirements. Together, these frameworks can help organizations build robust AI security programs. Whether a company adopts these voluntarily or complies out of necessity depends largely on its regulatory landscape. As NIST puts it:
"NIST will continue to align the AI RMF and related guidance with applicable international standards, guidelines, and practices."
Let’s break down the specifics of each framework.
Think of ISO/IEC 27001 as the foundation for creating secure systems. This global standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) is technology-neutral but provides essential tools like asset management, access control, and incident response. These elements form a baseline that organizations can adapt to protect their AI systems. For instance, ISO 27001's asset management principles can help catalog critical AI assets like training datasets, models, and research code - an essential step in securing AI.
In January 2025, Anthropic became the first company to achieve ISO/IEC 42001 certification, a standard specifically designed for AI management systems. This milestone shows how pairing ISO/IEC 27001's security practices with AI-focused controls can address vulnerabilities that traditional frameworks might miss. Similarly, OpenAI has completed SOC 2 Type II audits for its ChatGPT Enterprise and API services, demonstrating strong practices for handling customer data and fine-tuning processes.
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) 1.0 is all about managing AI risks through four key functions: Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage. Developed with input from over 240 organizations spanning industry, academia, and government, this framework acknowledges the socio-technical nature of AI. According to NIST:
"AI systems are inherently socio-technical in nature, meaning they are influenced by societal dynamics and human behavior."
In July 2024, NIST introduced the Generative AI Profile (NIST-AI-600-1), which helps organizations address the unique risks tied to large language models and other generative systems. While voluntary, the framework offers structured guidance to manage AI characteristics like safety, security, reliability, and fairness - making it a practical tool for building trustworthy AI systems.
The EU AI Act, which took effect on August 1, 2024, represents a significant shift by introducing the first legally binding rules for AI. Unlike voluntary frameworks, this regulation mandates compliance for companies operating in or providing AI services to the European Union. It categorizes AI systems into four risk levels - unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal - and assigns specific obligations based on these tiers.
To comply, organizations need to prepare technical documentation, including data lineage records and red-team testing logs. Starting August 2, 2025, developers of high-risk general-purpose AI (GPAI) models must conduct thorough testing and report serious incidents to the EU Commission. For global companies, this transition from voluntary standards to mandatory rules requires immediate action.
| Framework | Primary Focus | AI-Specific Coverage | Compliance Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27001 | General Information Security | Low (Technology-neutral) | Certifiable |
| NIST AI RMF | AI Trustworthiness & Risk | High (Socio-technical focus) | Voluntary |
| EU AI Act | Safety & Fundamental Rights | High (Risk-tiered) | Mandatory (Legal) |
| ISO/IEC 42001 | AI Management Systems | High (Process-oriented) | Certifiable |
Turning AI security theory into practice demands a clear and structured approach. Organizations must assess their current systems, create detailed policies, and train their teams to handle AI-specific threats effectively. As the Australian Signals Directorate explains:
"Securing an AI system involves an ongoing process of identifying risks, implementing appropriate mitigations, and monitoring for issues."
This is not a one-off task - it’s an ongoing process that evolves alongside your AI systems.
The first step is to adopt Testing, Evaluation, Verification, and Validation (TEVV) processes from the NIST AI Risk Management Framework. This involves assessing your AI systems both before deployment and on an ongoing basis. Developers should provide a detailed threat model that identifies potential attack vectors.
Before rolling out any AI model, ensure it undergoes rigorous inspection using AI-specific scanners in a secure environment to detect any tampering. Use cryptographic tools, digital signatures, and checksums to confirm that models, parameters, and data remain intact. Watch for signs of data drift or repetitive inputs, which could indicate model compromise or adversarial attacks. To protect sensitive components, store model weights in hardware security modules (HSMs) or similarly secure areas. Additionally, validate all input data to guard against prompt injection attacks, and bring in external experts for independent audits. The findings from these audits should guide the development of an AI security policy tailored to your organization’s needs.
A thorough audit lays the groundwork for crafting a comprehensive AI security policy. This policy should align with your broader risk management strategies and focus on four core functions: GOVERN, MAP, MEASURE, and MANAGE.
GOVERN establishes accountability, assigns roles, and fosters a culture where risk management is prioritized. As NIST points out:
"AI risk management should be integrated and incorporated into broader enterprise risk management strategies and processes."
MAP involves evaluating the context, data inputs, and potential impacts of each AI system before deployment. It’s essential to define your organization’s risk tolerance - how much risk you’re willing to accept to achieve your goals - since international standards don’t specify exact thresholds. Address third-party risks explicitly, as external data, software, or hardware can add layers of complexity. Ensure your AI systems demonstrate key attributes like reliability, safety, security, transparency, and accountability. Regularly update the policy to keep pace with evolving technology and standards.
With policies in place, the next step is ensuring your team is well-equipped to implement and adapt these measures. Given the rapid development of AI systems, training is crucial - especially since AI-related security incidents cost an average of $4.5 million to remediate. A shared responsibility model should involve collaboration across legal, product, data science, and security teams.
Start with foundational security training for all team members involved in AI projects, and provide advanced technical training for MLOps and engineering teams. Address common pitfalls like automation bias, where people may overestimate AI’s objectivity, and stress the importance of human oversight. Teams should also learn about AI-specific threats, including prompt injection, model poisoning, and evasion attacks - challenges that traditional cybersecurity measures often overlook.
Keri Pearlson, Senior Lecturer and Principal Research Scientist at MIT Sloan, highlights the issue:
"People are trying to figure out how best to use AI, but few are thinking about the security risks that come with it from day one."
Incorporate red-team exercises and threat-modeling workshops using frameworks like MITRE ATLAS to uncover vulnerabilities. Develop internal best-practice guides that outline expectations and regulatory risks specific to your organization’s AI applications. Maintain a living inventory of all models, datasets, and third-party AI services. Keep in mind that this is an ongoing effort - monitor and adapt your strategies as AI models evolve and new threats emerge.
Building strong AI security measures isn't just about protection - it's a smart business move. By adopting frameworks like ISO/IEC 42001 and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, companies lay the groundwork for growth while managing risks effectively. These frameworks aren't just technical checkboxes; they create real advantages, both competitive and regulatory, that drive sustainable business value.
The financial benefits are just as clear. Adopting recognized security standards acts like an insurance policy, helping to cut costs tied to security breaches and audit penalties. There's also a significant governance gap in AI, which presents both risks to manage and opportunities to seize. By 2026, it's predicted that half of the world's governments will require businesses to comply with specific AI laws and data privacy regulations. Early adoption of these measures isn’t just smart - it’s essential for staying ahead. Aligning security with business goals ensures companies can grow while meeting these emerging requirements.
To truly connect AI security with business success, trust must be built into every stage of product development. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework provides a practical roadmap for managing risks to individuals and society without stifling innovation.
Martin Tschammer, Head of Security at Synthesia, highlights the operational advantages:
"With Wiz, we can enable our engineers and development teams to confidently resolve issues on their own."
This self-sufficiency empowers teams to handle challenges directly, cutting down delays and speeding up deployment cycles. The investment in AI security pays off by reducing the costs of incidents and streamlining regulatory approvals. A focused approach can go a long way - just 20% of security controls can address 80% of an organization's AI-related risks.
To get started, organizations can adopt targeted tools like the Generative AI Profile (NIST AI 600-1) to address specific risks. Implementing an AI Bill of Materials (AI-BOM) helps track models, datasets, and third-party services, ensuring transparency and audit readiness as operations grow. Using a "Plan-Do-Check-Act" cycle for continuous monitoring ensures companies stay ahead of evolving regulations.
Certifications like ISO/IEC 42001 don’t just verify an organization’s AI governance - they also build trust. These third-party validations show clients and partners that the company is using AI responsibly and transparently, which is crucial for securing contracts in regulated industries. Beyond compliance, this level of transparency sets businesses apart from competitors.
Clear governance also helps clients and partners understand how decisions are made and which data drives those decisions. This is especially important for organizations operating across multiple regions. Adhering to international frameworks simplifies compliance with diverse legal requirements and demonstrates "reasonable care". Such alignment reduces trade barriers and makes it easier to expand into new markets without reworking compliance processes for every jurisdiction.
As SentinelOne puts it:
"Present frameworks as insurance policies that pay dividends through reduced incident costs and faster regulatory compliance."
To start, organizations can aim for quick wins - such as adopting the OWASP LLM Top-10 framework to address immediate vulnerabilities - before moving on to more comprehensive certifications. This step-by-step approach delivers early benefits and sets the stage for full compliance. By transitioning from lofty principles to enforceable norms, early adopters establish themselves as leaders in ethical AI, leaving competitors struggling to catch up.
It's time to prioritize AI security standards and build your AI product with a trusted partner. Unlike traditional software, AI systems come with unique risks because their dynamic data can unpredictably impact functionality and trust. Delaying action often leads to expensive, last-minute fixes rather than addressing issues upfront. The message is clear: proactive risk management is essential. As NIST warns:
"In cases where an AI system presents unacceptable negative risk levels – such as where significant negative impacts are imminent, severe harms are actually occurring, or catastrophic risks are present – development and deployment should cease in a safe manner until risks can be sufficiently managed."
Public trust is delicate and easily broken. Failing to manage risks early can lead to irreparable damage to an organization's reputation. Implementing TEVV (Testing, Evaluation, Verification, and Validation) early on avoids costly post-deployment corrections. This strategy not only protects your systems but also upholds civil liberties, fairness, and broader societal considerations before problems become deeply ingrained.
The AI security frameworks discussed earlier provide a solid starting point. These standards evolve alongside technological advancements, with NIST planning a formal review and global input by 2028 to stay aligned with rapid AI developments.
Risk management should begin at the "Plan and Design" phase, especially for systems that handle sensitive personally identifiable information (PII) or involve direct human interaction. Senior leadership must take accountability, ensuring alignment with proactive risk management strategies. Building this commitment requires a cultural shift across the organization. Additionally, documenting residual risks is critical to inform end-users about potential negative impacts before they engage with your systems. These measures build on the auditing and policy guidelines previously outlined.
Externally, regulatory frameworks are also taking shape. With 210 AI-related bills introduced across 42 U.S. states by late 2025, the push toward a unified national framework is gaining momentum. Organizations that adopt these standards early will be better equipped to navigate this evolving landscape. As NIST highlights:
"Addressing, documenting, and managing AI risks and potential negative impacts effectively can lead to more trustworthy AI systems".
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF), ISO/IEC 27001, and the EU AI Act each tackle AI security from unique angles:
In essence, NIST AI RMF offers a flexible, voluntary approach to managing AI risks, ISO/IEC 27001 focuses on comprehensive information security, and the EU AI Act establishes binding legal requirements for high-risk AI systems within the EU.
To effectively implement AI security standards, global organizations should consider adopting a recognized framework like the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF). This framework provides a structured way to identify, assess, and address risks throughout the AI lifecycle. Additionally, newer guidelines, such as the Cybersecurity Framework Profile for Artificial Intelligence, offer strategies to secure AI systems, detect vulnerabilities, and prevent misuse.
Building strong AI governance is just as critical. This means assembling cross-functional teams, performing regular risk assessments, and integrating security measures into development workflows. Technical standards from organizations like ETSI suggest best practices such as verifying model integrity and ensuring secure data handling. To maintain trust, businesses should document their processes, actively monitor for bias, and keep thorough audit logs.
Scalability and expertise also play a big role. Training teams in secure AI practices, automating vulnerability testing, and deploying real-time monitoring tools can help ensure compliance with frameworks like NIST and ETSI. By adopting a structured and standards-driven approach, organizations can create reliable AI systems that align with global security and regulatory requirements.
Building trust and reliability into systems from the start becomes much easier when businesses adopt AI security frameworks early. It ensures systems align with changing security standards, minimizes risk exposure, and protects sensitive information.
Taking a proactive approach to vulnerabilities doesn’t just shield operations - it helps companies stay ahead in a fast-moving market. Early adoption shows a dedication to responsible AI practices, boosting customer confidence and paving the way for lasting success.
.png)
.png)
